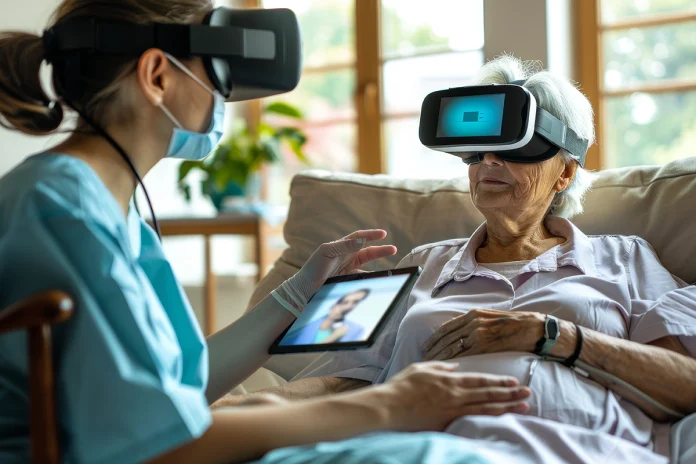
With artificial intelligence (AI) and its integration with wearable technology, many sectors have been transformed; healthcare is leading the front stage. AI wearables in hospitals provide a radical change in the way medical treatment is administered, watched over, and controlled.
Embedded with artificial intelligence, these smart medical devices are meant to gather, evaluate, and broadcast patient data in real time, thus providing hitherto unheard-of chances to increase operational efficiencies and patient outcomes.
The global wearable AI market size was valued at USD 31.00 billion in 2023. The market is projected to grow from USD 38.85 billion in 2024 to USD 260.29 billion by 2032
Though there are many advantages, the general acceptance of healthcare wearables also brings major issues that need to be resolved if we are to fully utilize them.
Benefits of AI Wearables in Hospitals
1) Enhanced Patient Monitoring
The capacity of AI Wearables in hospitals to constantly monitor patients is among its most important benefits. For real-time data, these gadgets track vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels, so arming medical practitioners.
Early identification of any health problems made possible by this ongoing surveillance helps to enable quick measures meant to avert complications and lower hospital readmissions. AI-powered wearables can notify medical workers in critical care environments of unexpected changes in a patient’s health, therefore guaranteeing prompt reactions that can save lives.
2) Improved Patient Outcomes
AI in healthcare holds great promise to raise patient outcomes. By adding artificial intelligence to wearables, hospitals may use predictive analytics to identify possible hazards to health and act before they become more serious.
AI systems can, for instance, examine wearables’ data to forecast a patient’s chance of acquiring illnesses including stroke, arrhythmias, or sepsis. Early identification of these hazards allows healthcare professionals to apply preventative actions, therefore improving patient outcomes and lessening the demand for hospital resources.
3) Operational Efficiency
AI in healthcare wearables also helps to ensure operational effectiveness. These technologies free healthcare personnel from manual data collecting and processing, therefore enabling them to concentrate on more important chores.
Wearable real-time data can also be included in electronic health records (EHRs), therefore simplifying documentation and lowering the possibility of mistakes. More accurate and current patient records resulting from this integration help to enable better-informed healthcare decisions.
4) Personalized Healthcare
Using artificial intelligence in wearable technology helps to provide individualized treatment in healthcare as well. Constant monitoring of a patient’s health indicators allows artificial intelligence systems to spot trends and patterns particular to that person.
More efficient and focused interventions result from healthcare providers customizing treatment regimens depending on a patient’s particular need thanks to this tailored data. Moreover, since they can access real-time data and insights from their wearables, patients are enabled to participate more actively in managing their health.
Common Challenges of AI Wearables in Hospitals
Data Privacy and Security
Maintaining data privacy and security is one of the main difficulties related to artificial intelligence wearables in hospitals. These devices gather enormous volumes of sensitive medical data, which, given improper protection, might be exposed to data breaches and cyberattacks.
Hospitals must follow strong cybersecurity policies to protect patient data, therefore including not only device security but also network and system security from which they are linked. In this respect, following laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is absolutely vital.
Integration With Existing Systems
Integration of AI Wearables with current hospital systems, including EHRs and clinical decision support systems, presents still another difficulty. Many hospitals run on antiquated systems that might not be compatible with the newest wearable technology.
Lack of interoperability might result in data silos whereby data gathered by wearables is not readily available or usable for healthcare providers. Hospitals have to make investments in modernizing their IT systems and implementing standardized protocols that enable smooth data flow across several platforms if they are to meet this difficulty.
Cost and Accessibility
Implementing AI Wearables in hospitals is expensive, especially for smaller institutions with tighter resources. Buying the tools, modernizing infrastructure, and staff training can all be expensive.
Furthermore, the expense of wearables could affect patient accessibility, particularly for those without enough insurance. Dealing with these financial issues calls for public and commercial sectors working together to guarantee that every patient, from all backgrounds, may benefit from artificial intelligence wearables.
Clinical Validation and Accuracy
The effectiveness of wearables in healthcare depends critically on the accuracy and dependability of AI algorithms applied in them. To guarantee they offer accurate and useful insights, these algorithms must thus be thoroughly clinically validated. Incorrect forecasts or inaccurate data could cause misdiagnoses and unsuitable therapy, therefore endangering patient safety. Consequently, validation of the performance of AI Wearables and the development of confidence among healthcare practitioners and patients depend on continuous research and clinical trials.
Conclusion
Offering many advantages including increased patient monitoring, improved outcomes, operational efficiency, and tailored care, AI wearables in hospitals mark a revolutionary development in healthcare. To effectively maximize this technology, though, issues with data privacy, system integration, cost, and clinical validation must be resolved.
Healthcare professionals, technology developers, and legislators must work together as artificial intelligence develops to guarantee that wearables are used safely and effectively, therefore improving the quality of life for individuals.